What is NAD+?

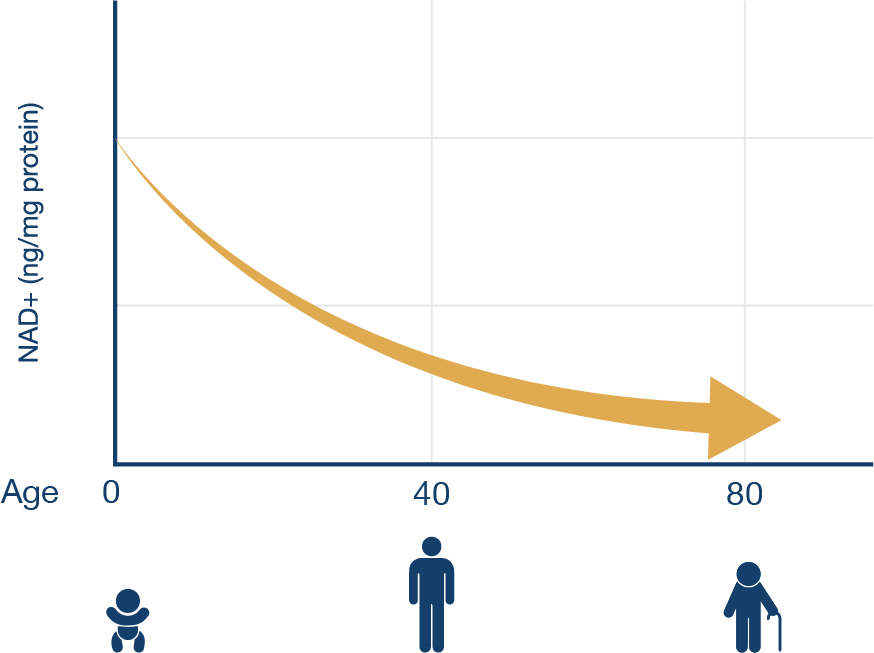
NAD+ Levels Decline with Age
What are NMN & NR?
NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) and NR (nicotinamide riboside), are two well-known precursors to NAD+. They become NAD+ through a series of chemical transformations. NR chemically transforms to NMN and then ultimately becomes NAD+ in our body.

Studies in mouse models have shown that supplementation with NMN can increase lifespan and decrease age-related frailty. This is likely due to NAD+ which can activate cellular repair pathways and which can improve a wide variety of physiological changes including restoring muscle function and athletic performance, improving brain regeneration and restoring energy levels etc.
NR vs NMN vs NAD+
| NR | NMN | NAD+ | |
| Dosage | Oral intake needs a much higher dose (a 180-pound man is like over 2000 mg per day) |
✔️ Oral dosage is much lower (around 200-400 mg per day) |
The molecule size is big. It is difficult to be taken up by cell. |
| Effects |
There was trending improvement in the vascular system, but there was no effect on endurance. |
✔️ It can help mitochondrial disease and increase endurance. |
High doses of NAD+ may inhibit the sirtuins, and PARP and interfere with DNA repair. |